Children
Children
We live in a noisy world. One in five teenagers are regularly exposed to high-decibel noise at rock concerts and nightclubs. About three quarters of people who go to nightclubs experience ringing in their ears afterwards. This condition is called temporary tinnitus and it usually lasts until your ears readjust to normal sound levels.
Noise-induced hearing loss
Hearing is an essential tool for learning speech, especially during a child’s first three years. So if you suspect a problem, it is important to have their hearing tested as soon as possible.
Types of hearing loss
Approximately six out of every 1000 children are born with some degree of hearing loss, while others develop hearing problems through infection or from environmental factors. These conditions can be categorised into two main types: conductive hearing loss and sensorineural hearing loss.
Conductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when the sound waves cannot travel freely through the outer ear, the tympanic membrane (eardrum) or the middle ear (ossicles). Obstructions to this pathway can cause a temporary blockage of sound transmission to the cochlea.
This can be as a result of:
• A build-up of wax in the ear canal
• A foreign object (such as the tip of a cotton bud) stuck in the ear canal
• Excess mucus in the Eustachian tube, caused by a cold
• Otitis media (infection of the middle ear)
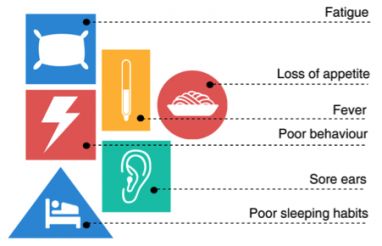
Middle ear infections
Approximately 80% of children experience at least one middle ear infection during childhood and nearly 50% of these children have recurring problems.
Please consult your doctor if your child displays any of these symptoms:
Sensorineural hearing loss
Sensorineural hearing loss occurs when the cochlea is unable to receive the signal. Unlike conductive hearing loss, which can be treated medically or surgically, a loss that affects the cochlea cannot be corrected.
The causes of permanent hearing loss in children include:
- Hereditary conditions that cause developmental abnormalities in the inner ear
- Some genetic disorders
- Exposure of the unborn baby to disease
- Loud noises, like firecrackers, rock concerts or personal stereos
- Injuries, such as concussion or skull fracture
- Certain diseases, including meningitis and mumps
